Cloud computing, not long ago considered a cutting edge technology, is now a common part of IT and developer operations. Cloud services offer scalable and elastic resources delivered via the Internet from a third-party provider.
Cloud-based services include compute power, storage, databases, messaging, and other building block capabilities that allow businesses to better run their IT applications without purchasing additional hardware and/or capital resources.
Most cloud providers operate on a pay-as-you-go model of business, so customers buy only the services they are truly using, rather than oversubscribing to meet peak availability.
There are three major cloud service models:
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): In IaaS, the vendor provides the infrastructure such as network, storage, or compute resources. The customer manages its own software on top of the vendor's hardware, usually including the operating system and up.
- Platform as a service (PaaS): In PaaS, the vendor provides the infrastructure and an application development platform that generally includes the operating system, database, and web server. Customers manage only their own applications.
- Software as a service (SaaS): SaaS is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor and made available to customers on a subscription basis.
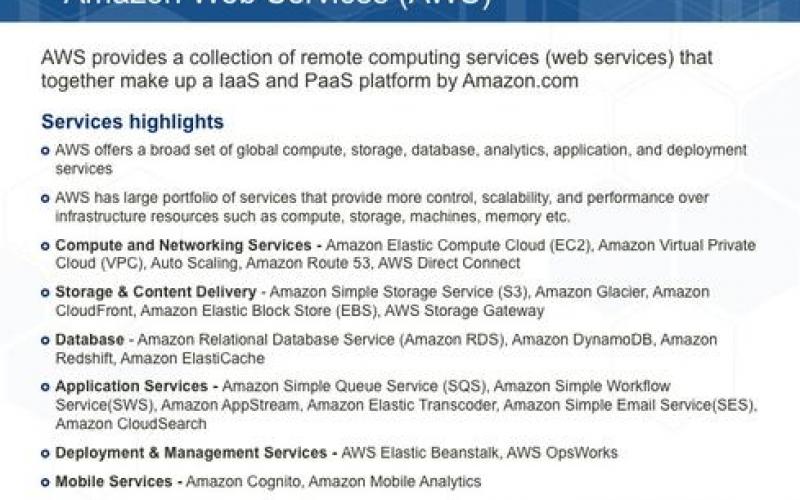
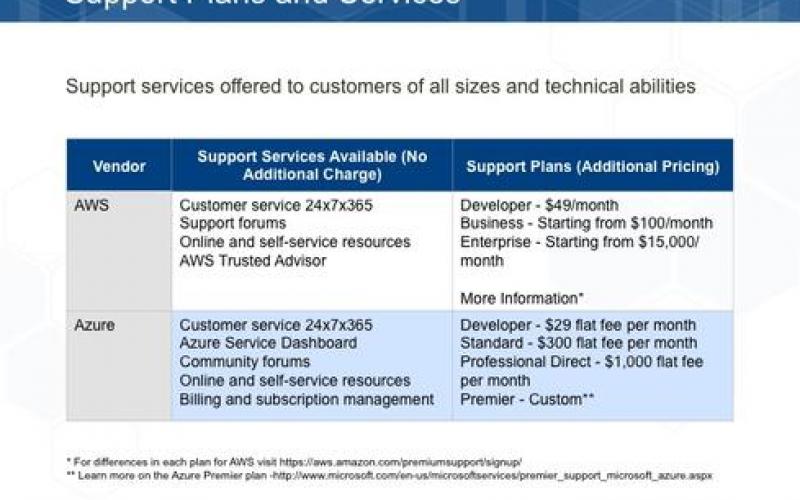
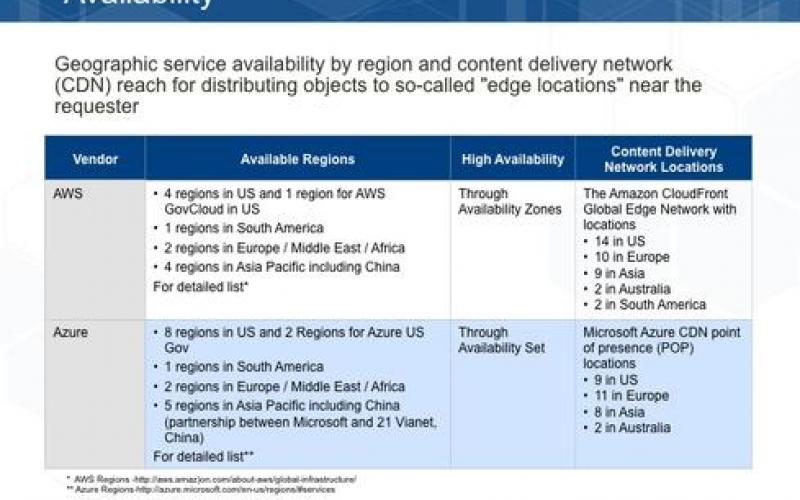
Two of the largest providers of IaaS and PaaS services are Microsoft with Azure and Amazon with AWS. These vendors both offer a rich and similar array of features and capabilities. However, they use different naming conventions for the same types of services, which can make it difficult to compare their services directly.
This report focuses on understanding the technical capabilities and differences between the two cloud vendors to help you make more informed decisions.